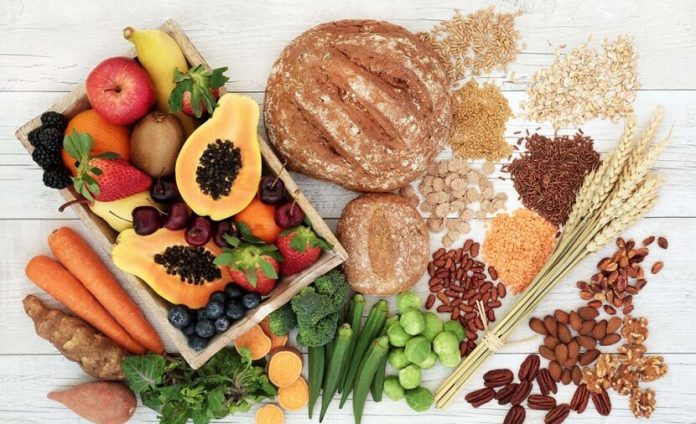
What is dietary fibre
Dietary fibre is a group of plant foods that pass through the stomach and small intestine undigested and reach the large intestine (colon) basically unchanged. While most other nutrients get digested and absorbed in the small intestine, fibre does not.
Dietary fibre (or “roughage”) is a complex mixture of different parts, including the carbohydrate parts – cellulose, hemicellulose, gums, mucilages, pectins and the non-carbohydrate part – lignin.
Some dietary fibre, found in fruits and legumes are digested (fermented) by bacteria in the colon. Other dietary fibre, found in grains and vegetables are not easily digested, but are expelled out of the colon, which they move through.
Important dietary fibre facts
- Fibres that are naturally intact in a plant are dietary fibre
- Most dietary fibres are one of the complex carbohydrates
- Insoluble fibre yields little if any energy, as it is not digested in the intestines
Why dietary fibre is important
The soluble dietary fibre in found in fruits and legumes provide protection against the following health conditions:
- heart disease – by lowering blood cholesterol levels
- diabetes – by lowering blood glucose levels
The insoluble dietary fibre found in grains and vegetables provides protection against the following health conditions:
- constipation – by promoting healthy bowel movements
- heart disease – by lowering blood cholesterol levels